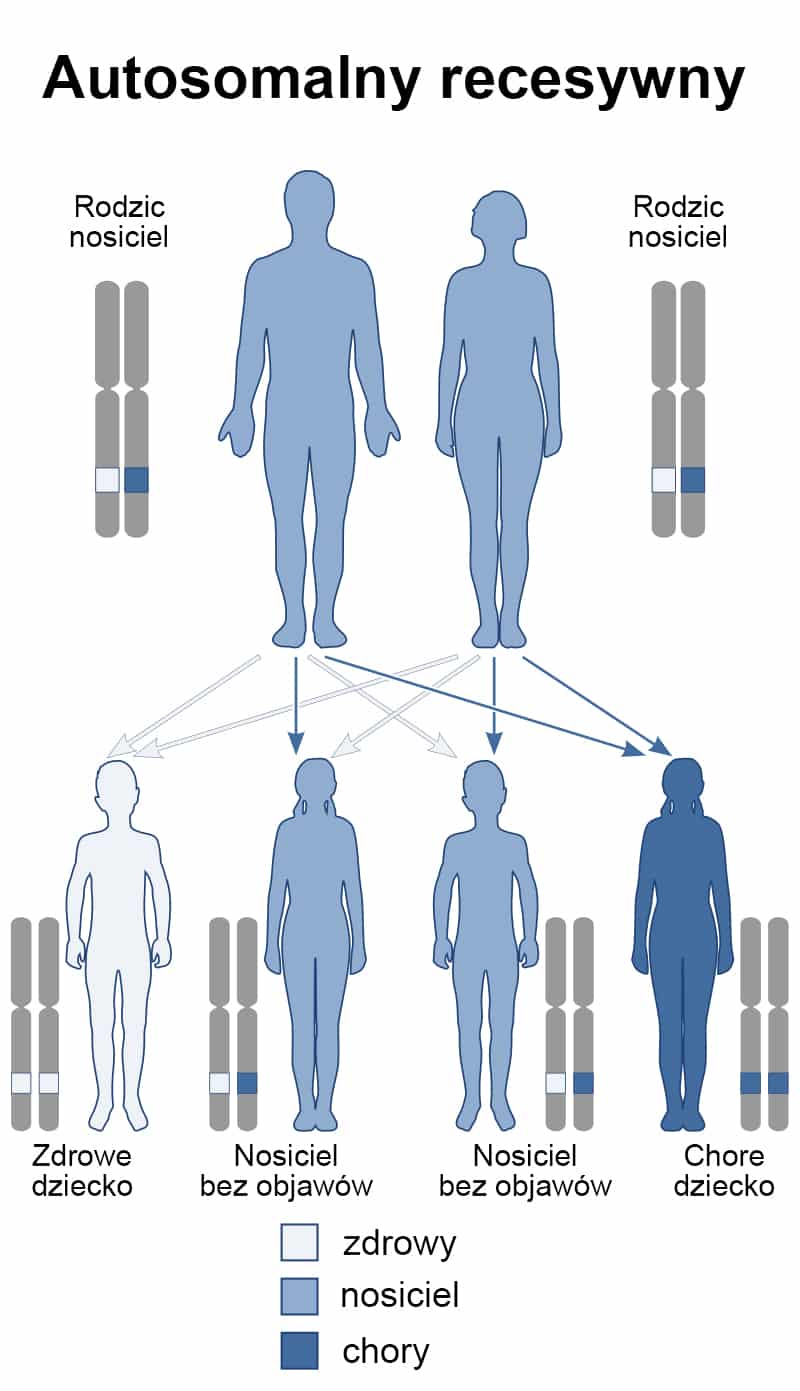
Mój przypadek Miopatii Mitochondrialnej nazywa się choroba POLG, poniżej na obrazku jest pokazane strzałkami gdzie mam uszkodzenia. Jak mówi badanie genetyczne wykonane w WUM.
„Badanie molekularne genu POLG ujawniło obecność trzech zmian: T251I, P587L, K1191N.
- Dwie z nich : T251I , K1191N są opisywane w literaturze jako recesywne mutacje patogenne i mogą odpowiadać za chorobę pacjenta.
- Charakter zmiany P587L jest nieustalony.
Wynik: badanie ujawniło zmiany: T251I, P587L, K1191N w stanie heterozygotycznym„
Dokładne wyniki badań wykonanych w klinice Warszawskiego Uniwersytetu Medycznego znajdziesz w dokumentach.
Mutacje w genie POLG: T251I, P587L, K1191N
- Mutacja T251I (strzałka wskazuje czerwone pola): Mutacja T251I to jedna z mutacji w genie POLG, która może prowadzić do miopatii mitochondrialnej związanej z tą konkretną zmianą genetyczną. Ta mutacja polega na zamianie nukleotydu tymidyny (T) na adeninę (A) w pozycji 251 w genie POLG. Ta zmiana może wpływać na funkcję enzymu DNA polimerazy gamma, co z kolei zaburza replikację mitochondrialnego DNA. Osoby z mutacją T251I mogą doświadczać różnorodnych objawów związanych z miopatią mitochondrialną, takich jak osłabienie mięśni, problemy neurologiczne i inne.
- Mutacja P587L (strzałka wskazuje niebieskie pola):: Mutacja P587L to kolejna mutacja w genie POLG, która jest związana z miopatią mitochondrialną. W tej mutacji prolin (P) jest zamieniana na leucynę (L) w pozycji 587 w genie POLG. Podobnie jak w przypadku innych mutacji w POLG, mutacja P587L wpływa na funkcję enzymu DNA polimerazy gamma, co prowadzi do zaburzeń w replikacji mitochondrialnego DNA. Osoby z mutacją P587L mogą mieć objawy związane z niewydolnością mitochondrialną i problemy neurologiczne.
- Mutacja K1191N (strzałka wskazuje czerwone pola):: Mutacja K1191N to kolejna mutacja w genie POLG. W tej mutacji lizyna (K) jest zamieniana na asparaginę (N) w pozycji 1191. Mutacja ta również wpływa na funkcję enzymu DNA polimerazy gamma, co prowadzi do defektów w replikacji mitochondrialnego DNA. Osoby z mutacją K1191N mogą prezentować objawy związane z miopatią mitochondrialną, takie jak osłabienie mięśni, problemy neurologiczne i inne objawy niewydolności mitochondrialnej.
Wszystkie te mutacje są przykładami zmian genetycznych w genie POLG, które wpływają na funkcję enzymu DNA polimerazy gamma i mogą prowadzić do miopatii mitochondrialnej. Ze względu na różnorodność mutacji w genie POLG, objawy i nasilenie choroby mogą się różnić w zależności od konkretnych zmian genetycznych. Diagnoza tych mutacji wymaga badań genetycznych przeprowadzonych przez specjalistów w dziedzinie genetyki medycznej.

Miopatia mitochondrialna z mutacją w genie POLG: Choroba, która wpływa na funkcjonowanie mitochondriów
Miopatia mitochondrialna to grupa rzadkich i kompleksowych chorób genetycznych, które wpływają na funkcjonowanie mitochondriów – małych struktur komórkowych odpowiedzialnych za produkcję energii. Jednym z rodzajów miopatii mitochondrialnych jest ta, która jest spowodowana mutacjami w jądrowym genie POLG (polymerase gamma-1), a nie w mitochondrialnym DNA (mtDNA). Choroba ta jest szczególnie interesującym przypadkiem, ponieważ wpływa na kluczową enzymatyczną jednostkę replikacji mitochondrialnego DNA.
Gen POLG: Kluczowa rola w funkcjonowaniu mitochondriów
Gen POLG koduje enzym zwanego DNA polimerazą gamma, który jest niezbędny do replikacji mitochondrialnego DNA. Mitochondrialne DNA jest odpowiedzialne za produkcję białek i enzymów niezbędnych do procesu produkcji energii w mitochondriach. Mutacje w genie POLG prowadzą do nieprawidłowej funkcji enzymu, co zaburza replikację mitochondrialnego DNA.
Objawy i przebieg miopatii mitochondrialnej z mutacją w genie POLG
Choroba POLG może mieć różnorodne objawy i nasilenie w zależności od konkretnych mutacji i ich wpływu na enzym polimerazy gamma. Typowe objawy tej choroby mogą obejmować:
- Niewydolność mitochondrialną: Pacjenci z miopatią mitochondrialną z mutacją w genie POLG często cierpią z powodu niewydolności mitochondrialnej, co prowadzi do chronicznego zmęczenia, osłabienia mięśni i braku energii.
- Problemy neurologiczne: Choroba może wpływać na układ nerwowy, co prowadzi do drżenia, ataksji (niekoordynacji ruchowej), zaburzeń mowy i innych problemów neurologicznych.
- Problemy z mięśniami: Miopatia mitochondrialna może powodować osłabienie mięśni, co objawia się jako trudności w chodzeniu, trudności w połykaniu i inne problemy związane z mięśniami.
- Zaburzenia wzroku i słuchu: Niektórzy pacjenci mogą doświadczać zaburzeń wzroku, słuchu lub innych problemów sensorycznych.
- Problemy z układem pokarmowym: Choroba może wpływać na układ pokarmowy, co może prowadzić do zaburzeń odżywiania i trudności w trawieniu.
- Zaburzenia psychiczne: Niektórzy pacjenci mogą doświadczać problemów z zachowaniem i zaburzeń psychicznych, takich jak depresja lub zaburzenia lękowe.
Diagnoza i leczenie
Diagnoza miopatii mitochondrialnej z mutacją w genie POLG jest często skomplikowana i wymaga specjalistycznych badań genetycznych. Leczenie jest zazwyczaj objawowe i skupia się na łagodzeniu objawów oraz poprawie jakości życia pacjenta.
Chociaż miopatia mitochondrialna z mutacją w genie POLG jest rzadką chorobą, to ważne jest, aby podkreślić znaczenie badań genetycznych i świadomości w dziedzinie chorób mitochondrialnych. Badania nad tą chorobą pomagają zrozumieć mechanizmy genetyczne wpływające na funkcjonowanie mitochondriów i mogą prowadzić do rozwoju bardziej efektywnych terapii w przyszłości.
| Amino Acid Substitution | Disease | Details | Frequency | Reference | Link to PubMed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T251I | 752 c→t (exon 3) | PEO | ar PEO. Found as compound with R309L, or 2354G insertion, or G848S in PEO. | 1 in 9 (11.11.5%) children with a combination of progressive neurological and hepatic failure, with a heterozygous frequency of 1.5% of Italian controls. | (Ferrari et al., 2005) | PubMed |
| PEO | Found in compound with R807P | (Del Bo et al., 2003) | PubMed | |||
| Infantile Hepatocerebral Syndrome | Frequently found in cis with P587L and compound in trans with L304R, V1106I, and R227W . | Not found in 250 control individuals | (Horvath et al., 2006) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | Found as compound in trans w/ S1176L, G848S, G785X, V1106I, R309L and R227W and cis w/ P587L. Also, T251I/P587L was found as a homozygous mutation. | (Lamantea and Zeviani, 2004) | PubMed | |||
| PEO and mtDNA deletions | Found in compound w/P587L/ R807P in1 pt. and w/P587L/ H932Y in a 2nd pt. A 3rd pt. was found in compound w/P587L only. The study includes 31 mitochondrial myopathy patients w/ mtDNA deletions. | 31 mitochondrial myopathy patients without any family history for the disorder | (Di Fonzo et al., 2003) | PubMed | ||
| Infantile Hepatocerebral Syndrome | 36% of patients with sporadic PEO with multiple mtDNA deletions carry mutations in one of the three genes associated with familial arPEO or adPE. Twinkle gene in 7% and POLG1 gene in 25% of our Italian and British patients with sporadic PEO. Found as compound in trans w/ R227W. Also, found as compound in cis with P587L. | 7 out of 27patients w/sporadic PEO compared to 250 controls individuals. | (Agostino et al., 2003) | PubMed | ||
| MNGIE | Found in cis with P587L and in trans w/N846S. | Van Goethem, 2003: Not found in 280 control chromosomes | ( Van Goethem et al., 2003c) | PubMed | ||
| Infantile Hepatocerebral Syndrome | Found in 1 of 9 infantile hepatocerebral syndrome patients. In cis with P587L and compound with R232G. | 9 infantile hepatocerebral patients of German and Italian descent. | (Ferrari et al., 2005) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | POLG molecular defects were found in 25% of patients with multiple mtDNA deletions and mitochondrial disease. Found in trans w/M603L and in cis with P587L. | 24 patients diagnosed with mitochondrial disease and having multiple mtDNA deletions compared to 100 controls in a Spanish population. | (Gonzalez – Vioque et al., 2006) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | Found in trans w/ G848S and in cis w/ P587L in a 75 y.o. male. | (Kollberg et al., 2005) | PubMed | |||
| Alpers | Found in trans w/ G848S and in cis w/ P587L. Also found in cis w/P587L and in trans w/R853Q in myocerebralhepatopathy patient. Also found as a heterozygous mutation with ataxia, ptosis, and neuropathy. | (Wong et al., 2008) | PubMed | |||
| Alpers | Found in cis w/ R232G and cis w/ P587L. | (Ashley et al., 2008) and a correction in (Ashley et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| PEO | Found in cis w/ P587L, with both mutations on each allele. A 2nd pt. found to have P587L in trans and A467T in cis. | (Stewart et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| mtDNA depletion | In cis w/P587L and in trans w/ E1136K | (Taanman et al., 2008) | PubMed | |||
| Hepatocerebral MDS | Found in cis with P587L and in trans with R232G | (Spinazzola et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| Restless leg syndrome, ptosis, diplopia, limb weakness, blurred vision | Found in trans with P587L. | (Aitken, et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| PEO | Found in trans with W748S andP587L | (Tzoulis, et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| PEO and mental retardation | Found in cis w/P587L and in trans w/ R275X | <0.5% in Dutch population | (Blok and van den Bosch et al., 2009) | PubMed | ||
| PEO, exercise intolerance, diabetes and a 2nd pt. w/ cataract and myopathy | Found in cis w/P587L and in trans w/ A467T | <0.5% in Dutch population | (Blok and van den Bosch et al., 2009) | PubMed | ||
| Ptosis | Found in cis w/P587L and in trans w/ G848S | <0.5% in Dutch population | (Blok and van den Bosch et al., 2009) | PubMed | ||
| Epilepsy and mental retardation | ad, Found w/P587L | <0.5% in Dutch population | (Blok and van den Bosch et al., 2009) | PubMed | ||
| Seizures, hypotonia, and developmental delay | Found w/P587L | (Burusnukul and de los Reyes, 2009) | PubMed | |||
| Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis | Found w/P587L, found in one 4 y.o. patient with autoimmune central nervous system disease | (Harris et al., 2010) | PubMed | |||
| SANDO | Found sporadically w/P587L and G848S in a 80 y.o. male | (Wiess and Saneto, 2010) | PubMed | |||
| Ptosis and myopathy | Found in cis with P587L and in trans with P648R in a 59 y.o. male with dysphagia, dysphonia, myopathy, ptosis, and mtDNA deletions. Father had same symptoms. | (Ferreira et al., 2011) | PubMed | |||
| PEO | Found in cis w/ P587L and in trans w/ H932Y in a 31 y.o. w/ neuropathy, PEO, ptosis, and COX deficiency. | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | ||
| Peripheral Neuropathy | Found in cis w/ P587L and in trans w/ H932Y in a 40 y.o. w/ peripheral neuropathy, ptosis, and muscle weakness. | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | Found in cis w/ P587L and in trans w/ G848S in an 80 y.o. w/ peripheral neuropathy, ptosis, and abnormal muscle histology | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | Found in cis w/ P587L and in trans w/ K1191N in a 39 y.o. w/ PEO, neuropathy, ptosis, and muscle weakness | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | ||
| Found in cis w/ P587L and in trans w/ N1157S in a 9 y.o. Symptoms not noted | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | |||
| Found in trans w/ G588D and in cis w/ P587L in a 6 y.o. w/ no symptoms noted | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | |||
| PEO | Found in compound with G848S in a 45 yo female with mtDNA deletions | Found in 160 French cohort of potential POLG patients | (Rouzier et al., 2013) | PubMed | ||
| P587L | 1760 c→t (exon 10) | PEO, neuropathy, and hearing loss | Found in trans w/ Q1236H in 2 different families and affected siblings | Filosto, 2003: not detected in 120 healthy control alleles. | (Filosto et al., 2003) | PubMed |
| PEO and mtDNA deletions | Found in compound w/T251I/ R807P in1 pt. and w/T251I/ H932Y in a 2nd pt. A 3rd pt. was found in compound w/T251 only. The study includes 31 mitochondrial myopathy patients w/ mtDNA deletions. | Di Fonzo 2003: Not found in 100 DNA samples from healthy Italians. | (Di Fonzo et al., 2003) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | Found in compound w/T251I and N864S in 2 sisters. | Van Goethem, 2003: Not found in 280 control chromosomes. | (Van Goethem et al., 2003c) | PubMed | ||
| Infantile Hepatocerebral Syndrome | Found in compound w/T251I and R232G | Ferrari et al., 2005 reported 1 in 9 (11.11.5%) children with a combination of progressive neurological and hepatic failure, with a heterozygous frequency of 1.5% of Italian controls. | (Ferrari et al., 2005) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | Found in compound w/T251I and G8484S in a 75 y.o. male | (Kollberg et al., 2005) | PubMed | |||
| PEO | Found as compound in trans w/ S1176L, G848S, G785X, V1106I, R309L and R227W and cis w/ T251I. Also, T251I/P587L was found as a homozygous mutation. | (Lamantea and Zeviani, 2004) | PubMed | |||
| PEO | Found in cis w/T251I and trans w/M603L. Also found in trans w/ R853W (no T251I). All had mtDNA deletions. | 24 patients diagnosed with mitochondrial disease and having multiple mtDNA deletions compared to 100 controls in a Spanish population. | (Gonzalez-Vioque et al., 2006) | PubMed | ||
| Alpers | Found in cis w/ T251I and in trans w/ G848S, also found as a hetero. mutation with ataxia, ptosis, and neuropathy | (Wong et al., 2008) | PubMed | |||
| Alpers | Found in trans w/R232G and in cis w/T251I. Also, in cis w/P589L and in trans w/W748S. | (Ashley et al., 2008) and a correction in (Ashley et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| Alpers | Found in cis with T251I with both mutations on each allele. Also, found in cis w/A467T and in trans w/T251I. | (Stewart et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| mtDNA depletion | In cis w/T251I and in trans w/E1136K | (Taanman et al., 2008) | PubMed | |||
| Hepatocerebral MDS | Found in cis w/ T251I and in trans w/ R232G | (Spinazzola et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| Restless leg syndrome, ptosis, diplopia, limb weakness, blurred vision | Found in trans with T251I. | (Aitken, et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| PEO | Found in cis with W748S and in trans with T251I. | (Tzoulis, et al., 2009) | PubMed | |||
| PEO and mental retardation | Found in cis w/ T251I and in trans w/ R275X | >0.5% of Dutch population | (Blok and van den Bosch et al., 2009) | PubMed | ||
| PEO, exercise intolerance, diabetes and a 2nd pt. w/ cataract and myopathy | Found in cis w/T251I and in trans w/A467T | >0.5% of Dutch population | (Blok and van den Bosch et al., 2009) | PubMed | ||
| Ptosis | Found in cis w/T251I and in trans w/G848S | >0.5% of Dutch population | (Blok and van den Bosch et al., 2009) | PubMed | ||
| PEO, ptosis, epilepsy, mental retardation, ataxia, polyneuropathy, and cataract | Ad, in cis w/T251I 3 patients: 4 yr. old w/PEO, ptosis, and motor delay development. A 10 yr. old with epilepsy and mental retardation, and 44 yr. old w/ cataract, polyneuropathy, myopathy, and ataxia | >0.5% of Dutch population | (Blok and van den Bosch et al., 2009) | PubMed | ||
| Seizures, hypotonia, and developmental delay | Found w/T251I | (Burusnukul and de los Reyes, 2009) | PubMed | |||
| Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis | Found w/T251I, found in one 4 yr. old patient with autoimmune central nervous system disease | (Harris et al., 2010) | PubMed | |||
| SANDO | Found sporadically w/T251I and G848S in a 80 yr. old male | (Weiss and Saneto, 2010) | PubMed | |||
| Ptosis and myopathy | Found in cis with T251I and in trans with P648R in a 59 y.o. male with dysphagia, dysphonia, myopathy, ptosis, and mtDNA deletions. Father had same symptoms. | (Ferreira et al., 2011) | PubMed | |||
| PEO | Found in cis w/ T251I and in trans w/ H932Y in a 31 y.o. w/ neuropathy, PEO, ptosis, and COX deficiency. | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | ||
| Peripheral Neuropathy | Found in cis w/ T251I and in trans w/ H932Y in a 40 y.o. w/ peripheral neuropathy, ptosis, and muscle weakness. | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | Found in cis w/ T251I and in trans w/ G848S in an 80 y.o. w/ peripheral neuropathy, ptosis, and abnormal muscle histology. | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | ||
| PEO | Found in cis w/ T251I and in trans w/ K1191N in a 39 y.o. w/ PEO, neuropathy, ptosis, and muscle weakness | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | ||
| Found in cis w/ T251I and in trans w/ N1157S in a 9 y.o. Symptoms not noted | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | |||
| Found in trans w/ G588D and in cis w/ T251I in a 6 y.o. w/ no symptoms noted | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed | |||
| K1191N | 3573 g→t (exon 22) | Alpers | Compound in trans with A467T | Not found in 250 control individuals | (Horvath et al., 2006) | PubMed |
| PEO | Found in trans w/ T251I and P587L in a 39 y.o. w/ PEO, neuropathy, ptosis, and muscle weakness | Found in a cohort of 2697 patients with suggestive clinical presentations of POLG deficiencies. | (Tang et al., 2011) | PubMed |
Źródło: National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS)
